The declaration of a nationwide flu alert signifies a significant increase in flu activity across the country. This alert is issued by public health authorities to raise awareness about the prevalence of the flu and its potential impact on public health. It serves as a warning to individuals, healthcare providers, and communities to take necessary precautions to prevent the spread of the flu virus.
The alert also prompts healthcare facilities to prepare for a potential surge in flu-related cases and ensure adequate resources are available to manage the situation effectively. The nationwide flu alert is typically based on data collected from various sources, including surveillance systems, healthcare facilities, and laboratory reports. It helps public health officials track the spread of the flu virus and identify trends in flu activity.
By issuing this alert, authorities aim to mobilize efforts to minimize the impact of the flu on the population and prevent further escalation of the outbreak. It is essential for individuals to heed the warnings associated with a nationwide flu alert and take proactive measures to protect themselves and others from contracting the virus.
Key Takeaways
- Nationwide flu alert declared, stay informed and take necessary precautions
- Understand the symptoms and risks of the flu to recognize and address them early
- Tips for staying healthy during flu season, including good hygiene and avoiding close contact with sick individuals
- Importance of vaccination in preventing the spread of flu and protecting oneself and others
- Know when to seek medical attention and the impact of flu on public health
Symptoms and Risks of the Flu
The flu, or influenza, is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that can lead to mild to severe symptoms and, in some cases, even death. Common symptoms of the flu include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, body aches, fatigue, and headaches. In severe cases, the flu can also cause complications such as pneumonia, bronchitis, sinus infections, and worsening of existing chronic medical conditions.
Certain groups of people are at higher risk of developing severe complications from the flu, including young children, elderly individuals, pregnant women, and individuals with underlying health conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or heart disease. It is crucial for these vulnerable populations to be especially vigilant during flu season and take proactive measures to reduce their risk of exposure to the virus. Understanding the symptoms and risks associated with the flu is essential for early detection and prompt intervention to prevent further spread of the virus.
Tips for Staying Healthy During Flu Season
During flu season, it is important to adopt healthy habits and preventive measures to minimize the risk of contracting the flu virus. Simple yet effective strategies include practicing good hand hygiene by washing hands frequently with soap and water, using alcohol-based hand sanitizers, and avoiding touching the face with unwashed hands. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and an adequate amount of sleep can help strengthen the immune system and reduce susceptibility to infections.
Furthermore, practicing respiratory etiquette by covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or elbow, staying home when feeling unwell, and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick can help prevent the spread of the flu virus. It is also advisable to clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces and objects in shared spaces to reduce the risk of contamination. By following these tips for staying healthy during flu season, individuals can contribute to minimizing the transmission of the flu virus within their communities.
Importance of Vaccination
| Metrics | Data |
|---|---|
| Number of lives saved | Millions |
| Reduction in disease prevalence | Significant |
| Cost savings in healthcare | Billions of dollars |
| Impact on herd immunity | Crucial |
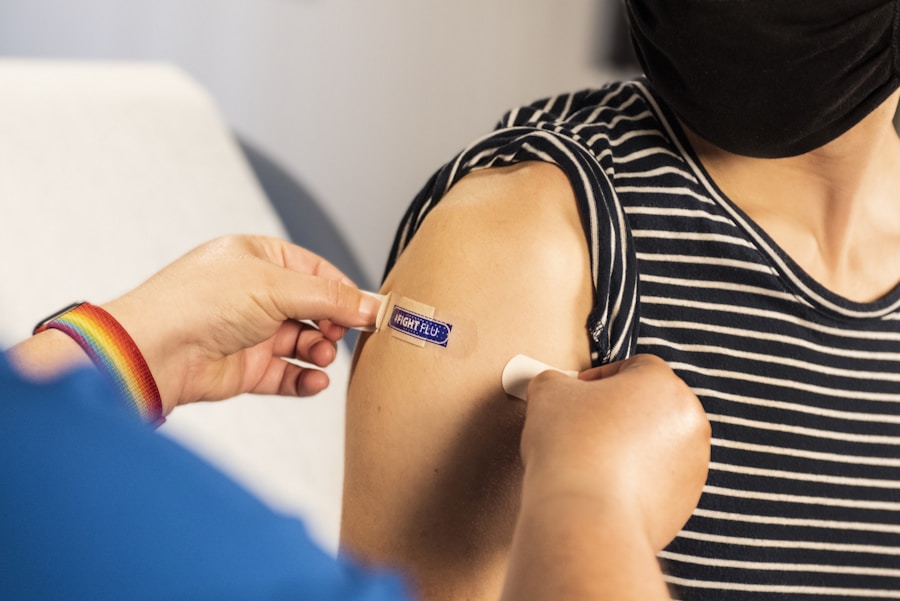
Vaccination against the flu is a crucial preventive measure that can significantly reduce the risk of contracting the virus and its associated complications. Annual flu vaccination is recommended for everyone six months of age and older, with rare exceptions. The flu vaccine helps stimulate the body’s immune response to develop protection against specific strains of influenza viruses that are anticipated to circulate during the upcoming flu season.
In addition to reducing the risk of illness, flu vaccination also plays a vital role in preventing hospitalizations, severe complications, and deaths related to the flu. It is especially important for individuals at higher risk of flu-related complications, including young children, elderly adults, pregnant women, and individuals with underlying medical conditions, to receive the flu vaccine. By getting vaccinated each year, individuals not only protect themselves but also contribute to community immunity, reducing the overall spread of the flu virus.
How to Protect Yourself and Others from the Flu
In addition to vaccination, there are several measures individuals can take to protect themselves and others from the flu. Practicing good respiratory hygiene by wearing a mask in crowded or high-risk settings, such as healthcare facilities or public transportation, can help reduce the spread of respiratory droplets containing the flu virus. Moreover, avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick and staying home when experiencing flu-like symptoms can prevent further transmission of the virus.
For individuals who are at higher risk of complications from the flu, it is essential to be proactive in seeking medical advice and promptly initiating antiviral treatment if flu symptoms develop. Additionally, promoting a supportive environment in workplaces and schools by implementing flexible sick leave policies and encouraging individuals to stay home when ill can help prevent outbreaks within these settings. By taking proactive measures to protect oneself and others from the flu, individuals contribute to safeguarding public health and minimizing the impact of flu outbreaks.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of the flu can be managed at home with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to alleviate symptoms, there are instances where seeking medical attention is necessary. Individuals experiencing severe or persistent symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, sudden dizziness, confusion, severe vomiting, or high fever should seek prompt medical evaluation. Furthermore, vulnerable populations at higher risk of complications from the flu should consult healthcare providers if they develop flu-like symptoms to receive appropriate care and treatment.
It is important for individuals to be aware of warning signs that indicate a need for medical attention and not delay seeking care when experiencing concerning symptoms. Healthcare professionals can provide guidance on managing flu symptoms, prescribe antiviral medications when indicated, and monitor individuals at higher risk for potential complications. Timely medical intervention can help prevent severe outcomes associated with the flu and ensure appropriate support for those affected by the virus.
The Impact of the Flu on Public Health
The flu has a significant impact on public health due to its potential to cause widespread illness, hospitalizations, and even fatalities during severe outbreaks. Each year, seasonal flu epidemics result in substantial economic burden and strain on healthcare systems as a result of increased healthcare visits, hospitalizations, and absenteeism from work and school. Furthermore, the flu can exacerbate existing health disparities by disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations who may have limited access to healthcare resources or face barriers in receiving timely medical care.
In addition to individual preventive measures such as vaccination and good hygiene practices, public health efforts play a critical role in mitigating the impact of the flu on communities. These efforts include surveillance systems for monitoring flu activity, public awareness campaigns promoting preventive measures, coordination of vaccination programs, and preparedness planning for potential flu outbreaks. By addressing the impact of the flu on public health through comprehensive strategies, authorities aim to minimize illness burden and protect population health during flu seasons.
In conclusion, understanding the implications of a nationwide flu alert is essential for individuals and communities to take proactive steps in staying healthy during flu season. By recognizing the symptoms and risks associated with the flu, adopting preventive measures such as vaccination and respiratory hygiene practices, knowing when to seek medical attention, and acknowledging the broader impact of the flu on public health, individuals can contribute to reducing the spread of the virus and safeguarding community well-being.

